HVAC
13
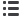
10.1.4 HVAC SYSTEM LAYOUT AND WORKING
WORKING
The HVAC system is similar to a conventional auto-
motive HVAC system. It consists of a Compressor, a
Condenser, and an evaporator. System wise it can
be divided as low pressure side and the high pres-
sure side, which is divided at the evaporator, more
precisely at the expansion valve housed in it.
REFRIGERANT CYCLE
The compressor compresses the refrigerant R134a,
increasing its pressure and temperature. This high
pressure hot vapor is then made to pass through the
condenser
(condenser is cooled by the passing am-
bient air),
where it gives its latent heat to turn to
liquid, the drop in temperature is small, as most of
the heat lost will be latent heat resulting in change of
state to liquid
A receiver drier which is integrated in the condenser
is used to filter out the moisture and also allows only
liquid to flow further to the Thermal Expansion Valve
valve). The high pressure low temperature liquid
then expands in the TXV Valve where the refrigerant
pressure drops considerably, which also results in a
drop of temperature.
This cold low pressure liquid is circulated through the
evaporator coil, where it absorbs the heat of the am-
bient air made to pass through it by forced circulation
of the blower. The liquid refrigerant absorbs the la-
tent heat required to change to vapour state and
turns to vapour. There is no considerable change in
temperature as the heat absorbed by the refrigerant
is only latent heat. This vapour then flows to the
compressor and the cycle continues.
ENGINE COOLANT FLOW
A small amount of hot coolant from the engine is
made to pass through the heater coil keeping it at a
higher temperature all the time. From the heater coil
the coolant is flows to the water pump and again cir-
culated through the Engine.
AIR FLOW
The air is drawn in through the inlet duct due to the
suction created by the blower. The blower forces
either the ambient air or the cabin air depending on
the mode selected
(Fresh Air mode or Recirculation
mode)
to flow over the evaporator which lowers the
temperature of the ambient air. The incoming air also
gets dehumidified as the moisture condenses when
the air flows over the cold evaporator fins. This cold
de-humified air is then mixed with the hot air (
if re-
quired)
to attain the temperature selected by the
occupant; the mixing control is done by the heater
door opening