STEERING
19
7.3.3.6 WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Wheel alignment is a procedure of aligning
wheels according to the specifications.
The purpose of these adjustments is to give
maximum tire life and vehicle-travel that is straight
and true when driving along a straight and level
road. A correct wheel alignment is necessary
because it affects directional stability, tire tread
wear and vehicle’s safety.
Warning signs of improper wheel alignment
include steering wheel shimmy, a constant
steering pull to one side, tire squeal noises when
making turns, excessive vibration as speed
accelerates, and changes in direction after a car
has hit a bump on the road. If any of the above
symptoms are noticed, wheel alignment becomes
necessary.
Wheel alignment should be done at the time of
fitting new tires and thereafter at regular intervals.
Wheels which may be only a fraction out of
alignment can scrub or drag along the road
instead of rolling along it.
Normally overall wheel alignment refers to the
procedures used to check and adjust the steering
system, including the camber, caster, and toe.
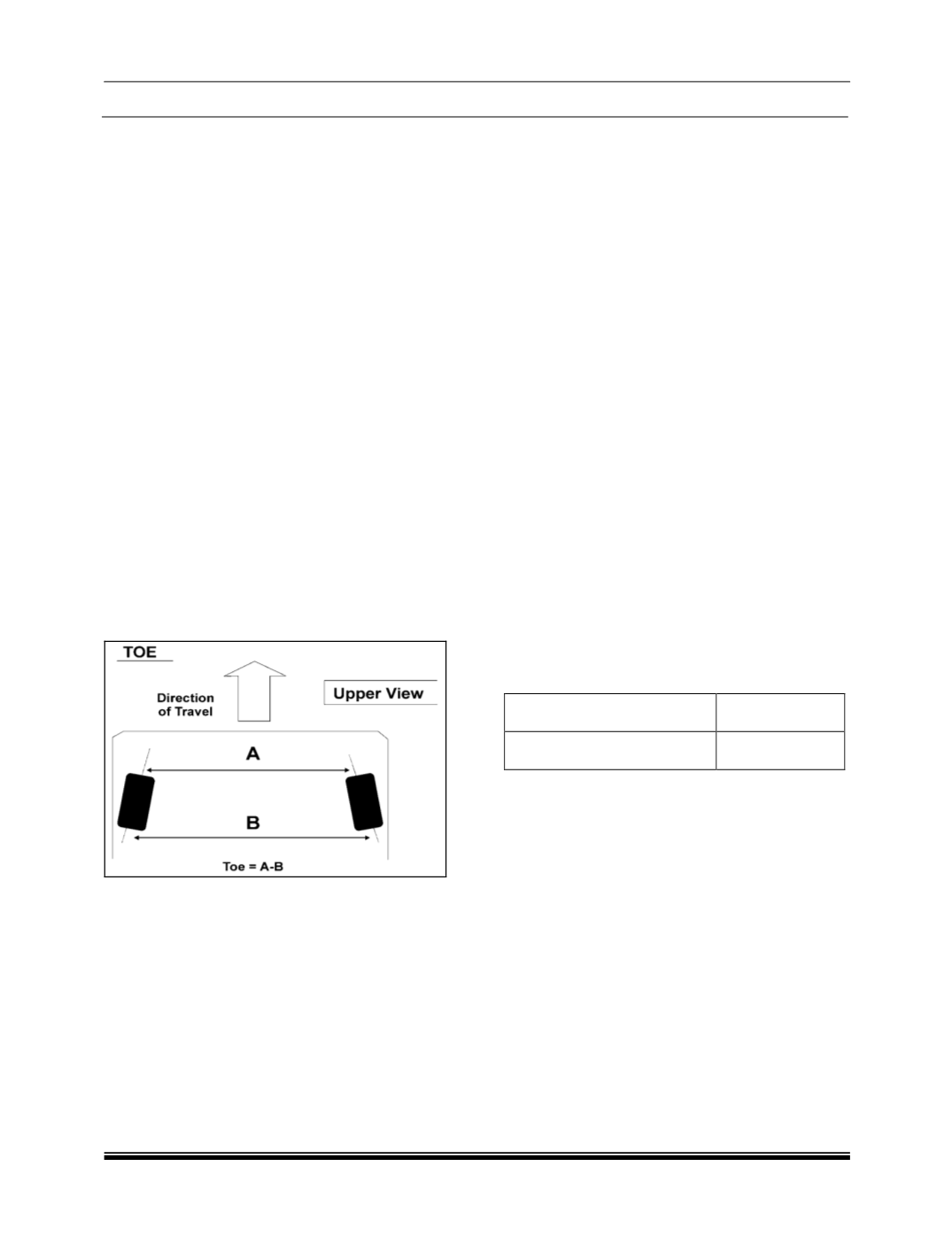
Basically toe is a measurement of how much the
front and/or rear wheels are turned in or out from
a straight ahead position. When the wheels are
turned in, toe is positive (+). When the wheels are
turned out, toe is negative (-).
The purpose of toe is to ensure that the wheels
roll parallel. Toe also serves to offset the small
deflections of the wheel support system that occur
when the vehicle is rolling forward. In other words,
with the vehicle standing still and the wheels set
with toe-in, the wheels tend to roll parallel on the
road when the vehicle is moving.
Toe settings affect three major areas of
performance:
(a) Tyre wears
(b) Straight-line stability and
(c) Vehicle handling characteristics
Following precautions are to be taken before
commencing wheel alignment:
1. Car should be unladen and parked on level
surface.
2. Front and rear tires should be inflated to
correct pressure (28 and 32 psi respectively)
3. Ensure that bushes in the front/rear
suspension are in satisfactory condition.
4. Ensure that front rear & suspension fasteners
are tightened to their specified torques.
5. Also ensure that there is no visible damage to
any of the suspension parts like lower link
bushes and struts.
6. Ensure that there is no play in steering
linkages and suspension ball joints.
7. Ensure no tyre wear on any wheels. If so
replace the respective tires.
For steering geometry adjustment (wheel
alignment) on vehicle – Refer Wheels & Tyres
section in Suspension chapter
Wheel lock angle (Outer)
31.96°
Wheel lock angle (Inner)
36.59°