BRAKES
15
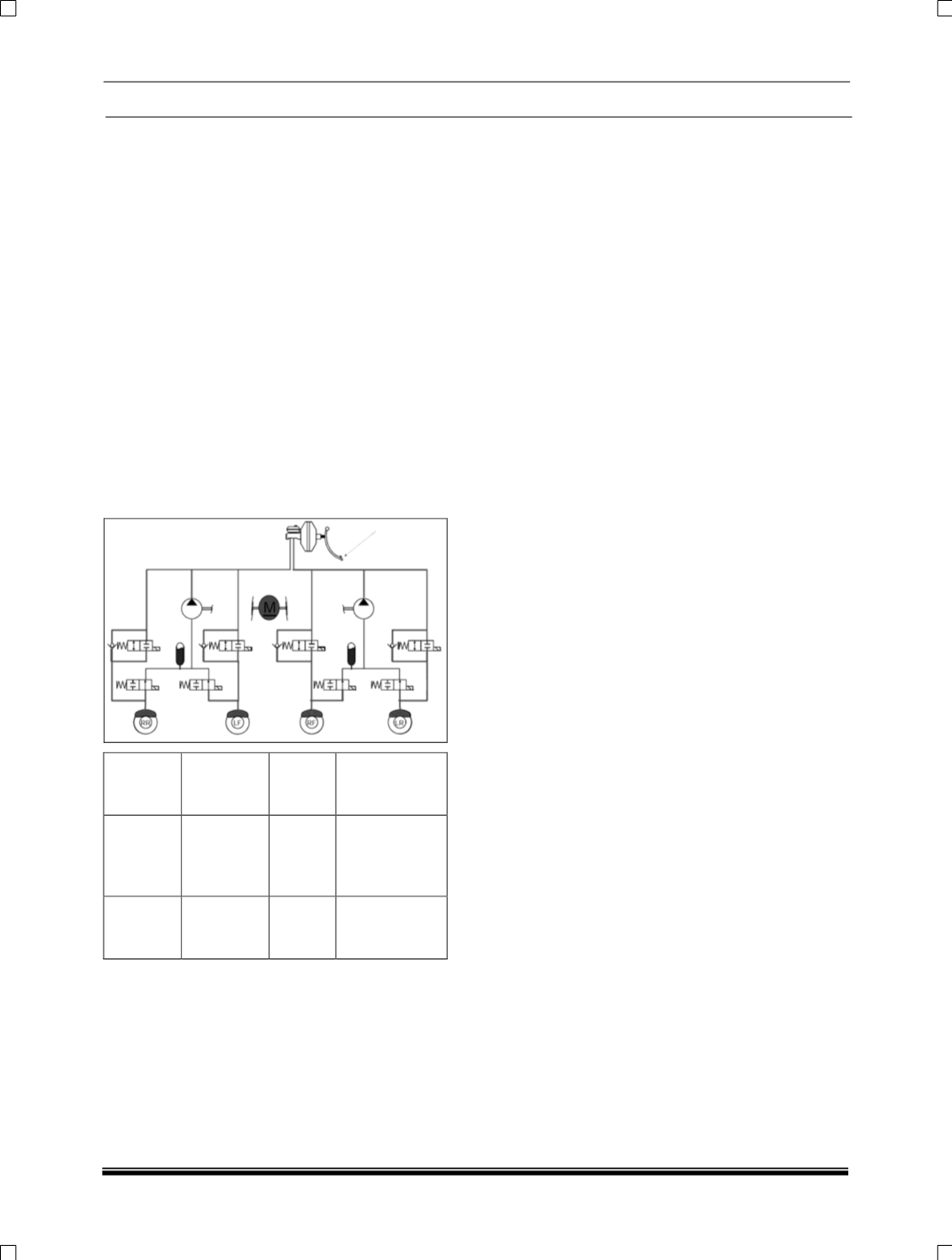
3. Pressure Reduction Phase:
If the ECU detects that the % Slip relative to the
other wheels and vehicle reference speed is still
increasing during the pressure hold phase and the
wheel is tending further towards lock it will start
the pressure reduction phase as the existing
brake pressure in the wheel brake is too high. It
will activate the relevant outlet valve within the
hydraulic modulator, switching it from its normally
closed position to open. This will allow fluid to
pass from the wheel brake into the accumulator
chamber within the modulator. At the same time
the ECU will activate the return pump integrated
into the modulator to draw fluid from the
accumulator and wheel brake and return it to the
TMC. This fluid being returned to the TMC is what
is felt as the pulsations at the pedal, and the
amplitude of the pulsations is relative to the
amount of fluid that needs to be reduced.
Pressure reduction will continue until controlled
wheel returns to the vehicle reference speed.
Solenoid
valve
Electricity
status
Valve
open
Open- close
channel
close
INLET
ON
CLOSE
Master
cylinder
Wheel
cylinder
OUTLET
ON
OPEN
Wheel
cylinder
Reservoir
D.FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION:
If the ABS system detects any fault that may
adversely affect its performance it will switch to a
fail safe shut down mode. When this happens the
electricity supply to the solenoid valves is
deactivated, stopping control signal output, this
causes the valves to switch to their default state.
(Open for inlet valves / Closed for Outlet valves)
The System will light the relevant warning lamp at
the same time to inform the driver the vehicle has
either an ABS or an ABS and EBD failure.
In this condition, the conventional hydraulic brake
circuit will still function, allowing brake pressure to
reach all wheels. It should be noted that with an
ABS fault it will be possible to lock the wheels and
in the Case of an EBD failure the brake force
proportioning between front and rear will no
longer function and hence rear wheel lock is
possible before front.