ELECTRICAL
196
8.27 FUSE AND RELAY BOX DETAILS
CHECKING FUSES:
If any electrical unit in the vehicle has stopped
functioning, fuses should be checked first.
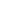
A blade type fuse has test taps provided to allow
checking of the fuse itself without removing it from
the fuse block. The fuse is okay if the test light
comes on when its one lead is connected to the
test taps (
one at a time
) and the other lead of the
test light is grounded. Remember to turn the
ignition switch to ON to ensure all circuits are live.
CAUTIONS IN EVENT OF BLOWN FUSE
When a fuse is blown, there are two probable
causes. One is that it is blown due to flow of
current exceeding its rating. The other is that it is
blown due to repeated on/off current flowing
through it. Which of these two causes were
responsible for the fuse to be blown can be
determined by visual check as described below.
1. Fuse blown due to current exceeding rating
The illustration shows the state of a fuse blown
due to this cause. In this case, do not replace the
fuse with a new one quickly since a current heavy
enough to blow the fuse has flowed through it.
First, check the circuit for shorts and check for
abnormal electric parts. After correcting shorts or
replacing parts, use only a fuse of the same
capacity as a replacement. Never use a fuse of
larger capacity than the original fuse. If a larger
capacity fuse is used, electric parts or wiring could
be damaged, or could start a fire.
2. Fuse blown due to repeated turning current on
and off:
The illustration shows the state of a fuse blown
due to repeated current on/off. Normally, this type
of problem occurs after a fairly long period of use
and is less frequent than above. In this case,
simply replace with a new fuse of the same
capacity.
CHECKING RELAYS:
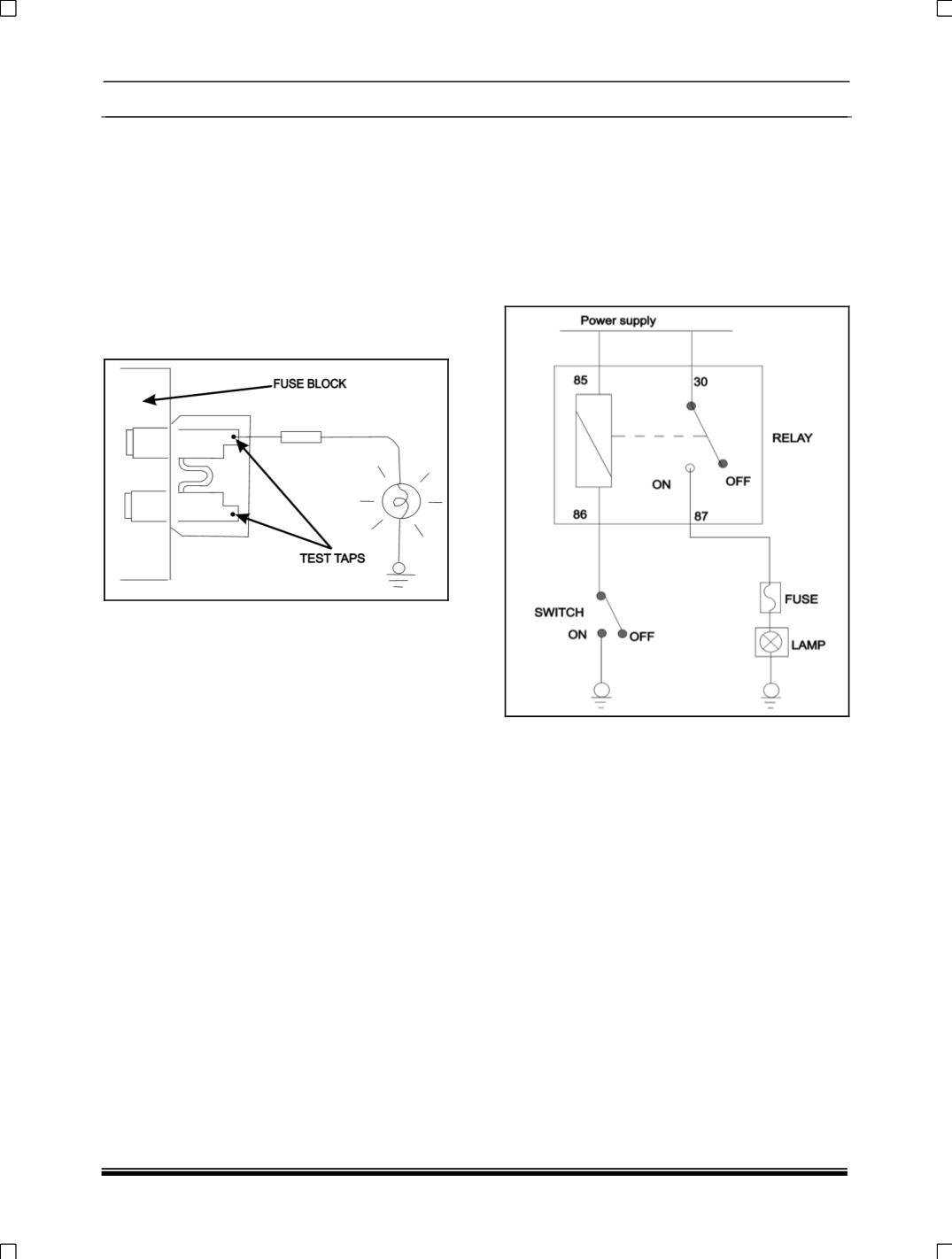
1.
By using a relay, a heavy current can be
turned on and off by a switch using much less
current. For example, in the circuit shown here,
when the switch is turned on (
closed
), current
flows to the coil of the relay. Then, its contact
is turned on (
closed
) and the light comes on.
The current flowing through the switch is much
less than that for the light.
2.
Relays may be classified as the normally
open-type or the normally closed-type,
depending on their contact construction.
NOTE:
The De-energized state means that no
current is flowing through the coil. The energized
state means that current is flowing through the
coil.
(a) The normally open-type
When a normally open relay as illustrated
here is checked, there should be no
continuity between terminals 30 and 87
when the relay is de-energized. There
should be continuity between terminals 30
and 87 when battery voltage and ground
are applied to terminals 85 and 86. The
relay condition is determined by this check.
NOTE:
Check the relay in both condition, i.e.
energized and not energized