STEERING
2
7.1.3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The
EPAS
(electrical power assisted steering -
column mounted) is made up of the following
components
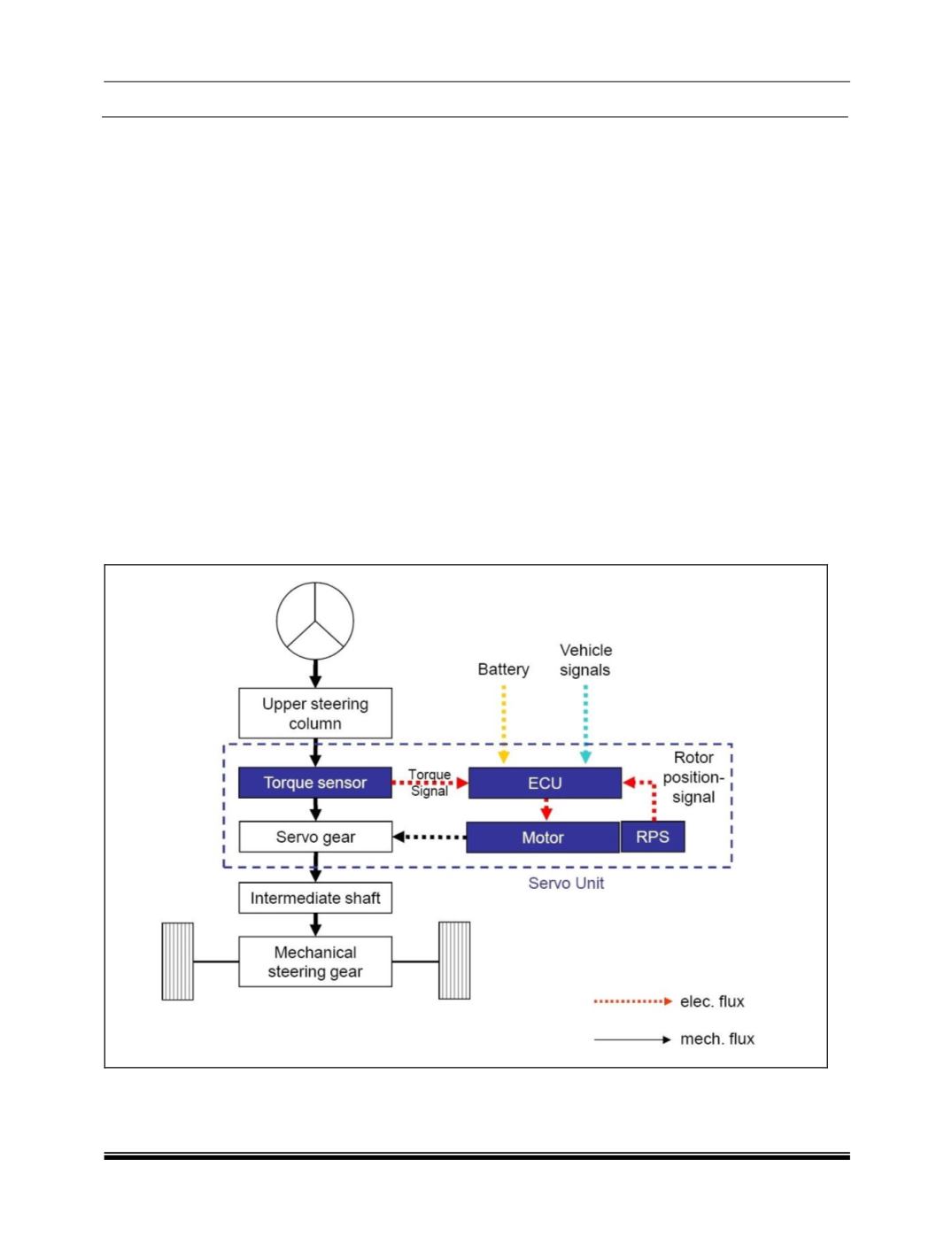
The system consists of the steering column (2)
and a servo unit (4). The steering torque is
transmitted via the intermediate shaft (5) with
universal joints (6) to the mechanical rack and
pinion steering (7). Sensor technology and torsion
bar are next to the helical gear drive in the servo
unit (4). The helical gear drive converts the
support torque generated by the servo motor (4)
and transmits it to the intermediate shaft (5).
The support torque and operating torque of the
steering wheel generated are transmitted via the
intermediate shaft (5) to the rack-and-pinion
steering (7) and then to the wheels.
If the vehicle power supply or electrical supply
fails, then the vehicle can still be steered due to
the mechanical connection between the steering
wheel and the wheels being steered.
FUNCTION
The torque sensor in servo unit registers the
steering torque and steering speed once the
driver performs a steering motion.
All data (including the vehicle signals such as
engine speed, vehicle speed, ignition signal) is
transmitted to the control unit (ECU). This then
calculates the necessary support torque and on
the basis of the calculated results, controls the
servo motor (4).
A rotor position sensor is attached to the servo
motor (4). An index sensor is integrated in the
torque sensor.
The control unit (3) uses the integrated index
sensor and the rotor position sensor to calculate
the steering wheel’s steering angle.
Depending on the programming, the steering
wheel’s angle signal can be sent back to the
vehicle.
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF EPAS SYSTEM
: